It is a program with following features:
● An operating system is a program that acts as an interface between the software and the computer hardware.
● It is an integrated set of specialised programs that are used to manage overall resources and operations of the computer.
● It is specialised software that controls and monitors the execution of all other programs that reside in the computer, including application programs and other system software.
Objectives of Operating System
● To make a computer system convenient to use in an efficient manner
● To hide the details of the hardware resources from the users
● To provide users a convenient interface to use the computer system
● To act as an intermediary between the hardware and its users and making it easier for the users to access and use other resources
● To manage the resources of a computer system
● To keep track of who is using which resource, granting resource requests, according for resource using and mediating conflicting requests from different programs and users
● To provide efficient and fair sharing of resources among users and programs
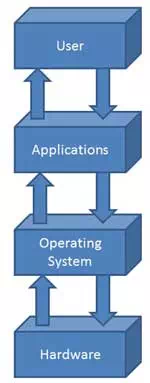
Characteristics of Operating System
● Memory Management — keeps tracks of primary memory i.e. what part of it is in use by whom, what part is not in use etc. and allocates the memory when a process or program requests it.
● Processor Management — allocates the processor(CPU) to a process and deallocates processor when it is no longer required.
● Device Management — keeps track of all devices. This is also called I/O controller that decides which process gets the device, when, and for how much time.
● File Management — allocates and de-allocates the resources and decides who gets the resources.
● Security — prevents unauthorized access to programs and data by means of passwords and similar other techniques.
● Job accounting — keeps track of time and resources used by various jobs and/or users.
● Control over system performance — records delays between request for a service and from the system.
● Interaction with the operators — The interaction may take place via the console of the computer in the form of instructions. Operating System acknowledges the same, does the corresponding action and informs the operation by a display screen.
● Error-detecting aids — Production of dumps, traces, error messages and other debugging and error-detecting methods.
● Coordination between other software and users — Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, assemblers and other software to the various users of the computer systems.